Greek diplous – double; kaulos – stem; lobion − lobe; an allusion to the dimorphic pseudobulbs in some species
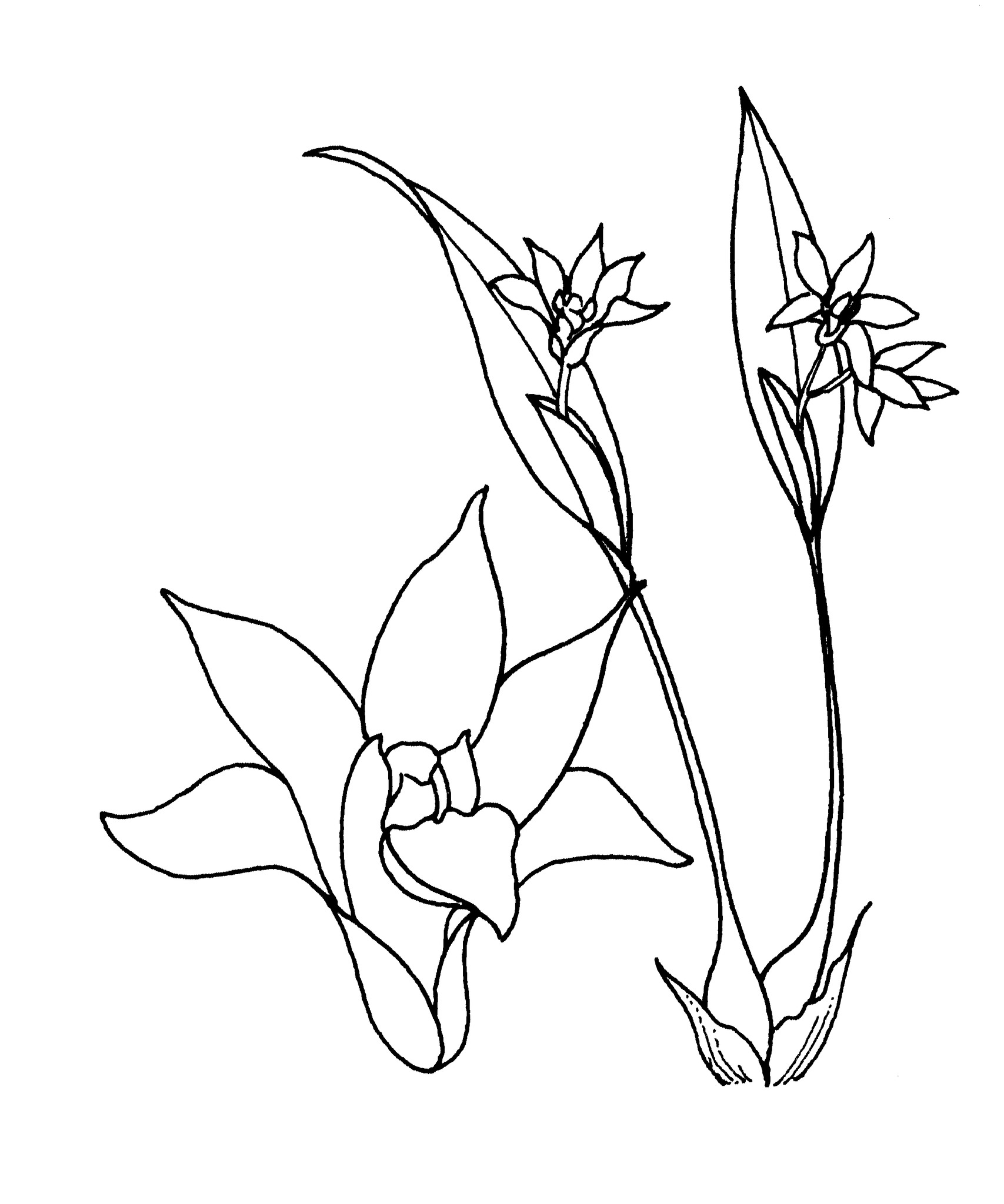
Epiphytic or epilithic herbs, sympodial, with creeping rhizomes. Stems thickened into pseudobulbs, sometimes of 2 types, either ovoid to pear-shaped or rather slender in flowering growths. Leaves apical, solitary, thin to leathery, mostly stalkless. Inflorescences terminal racemes, sheathed at base. Flowers resupinate, usually solitary, short-lived, appearing in succession, small to large, white, yellow or pink. Sepals similar, often narrow, dorsal free, laterals fused to column foot forming a chin-like extension. Petals usually slightly smaller than sepals, free. Labellum usually 3-lobed, joined to tip of column foot. Column short, winged, with a long foot. Pollinia 4, in 2 pairs.
A few of the miniature white, spider flowered species are sometimes grown by enthusiasts.
About 70 species from SE Asia, Indonesia, New Guinea, Fiji and Australia.
Short-lived flowers opening successively and turning pink with age; flowering and nonflowering pseudobulbs often different in form.
Source: (2005). Orchidaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 5. Flowering plants. Monocotyledons. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
