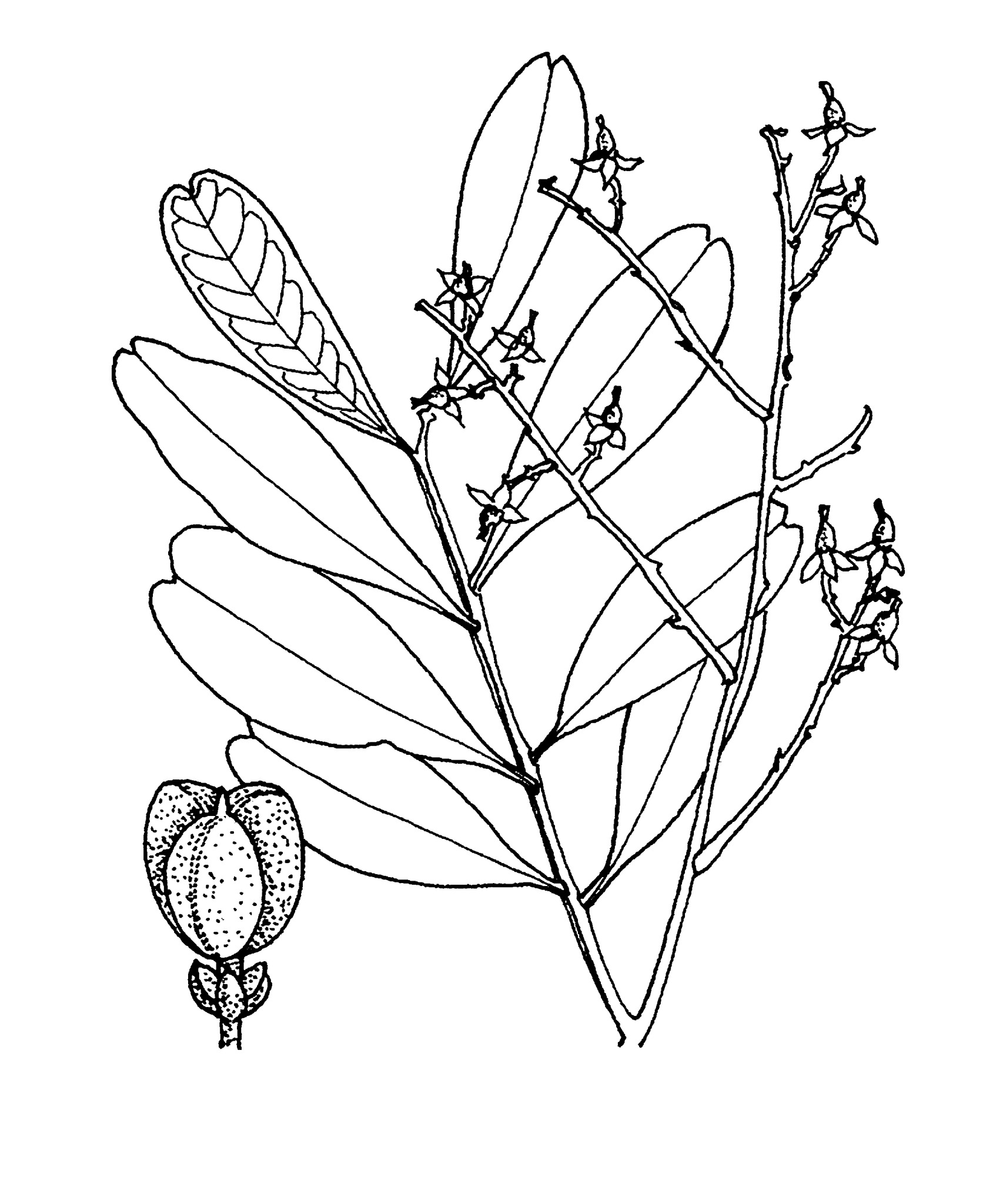
From Cupania, named after Italian monk, Francesco Cupani (1657–1710), author of the book Sicilian Plants, and -opsis, resembling.
Evergreen trees. Branches with pronounced lenticels. Leaves alternate, evenly pinnate. Leaflets alternate to more or less opposite, margins entire or toothed. Flower clusters axillary. Flowers unisexual, the sexes on the same or different plants. Calyx in 2 rows, the outer sepals smallest. Petals 5, each with 2 scales. Disk wavy. Stamens 6-10.ovary with 1 ovule per chamber. Fruit a shortly stalked, 3-lobed, 3-chambered dehiscent capsule.
Rainforest trees mostly grown in older botanic and public gardens and special collections, sometimes as street trees.
66 species from the Pacific region. Australia has 11 endemic species.
Fresh seed.
Insides of capsules velvety-hairy and sepals mostly silky outside.
Source: (2002). Sapindaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 3. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 2. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
