From the Greek saurus — lizard, podus — foot, application obscure.
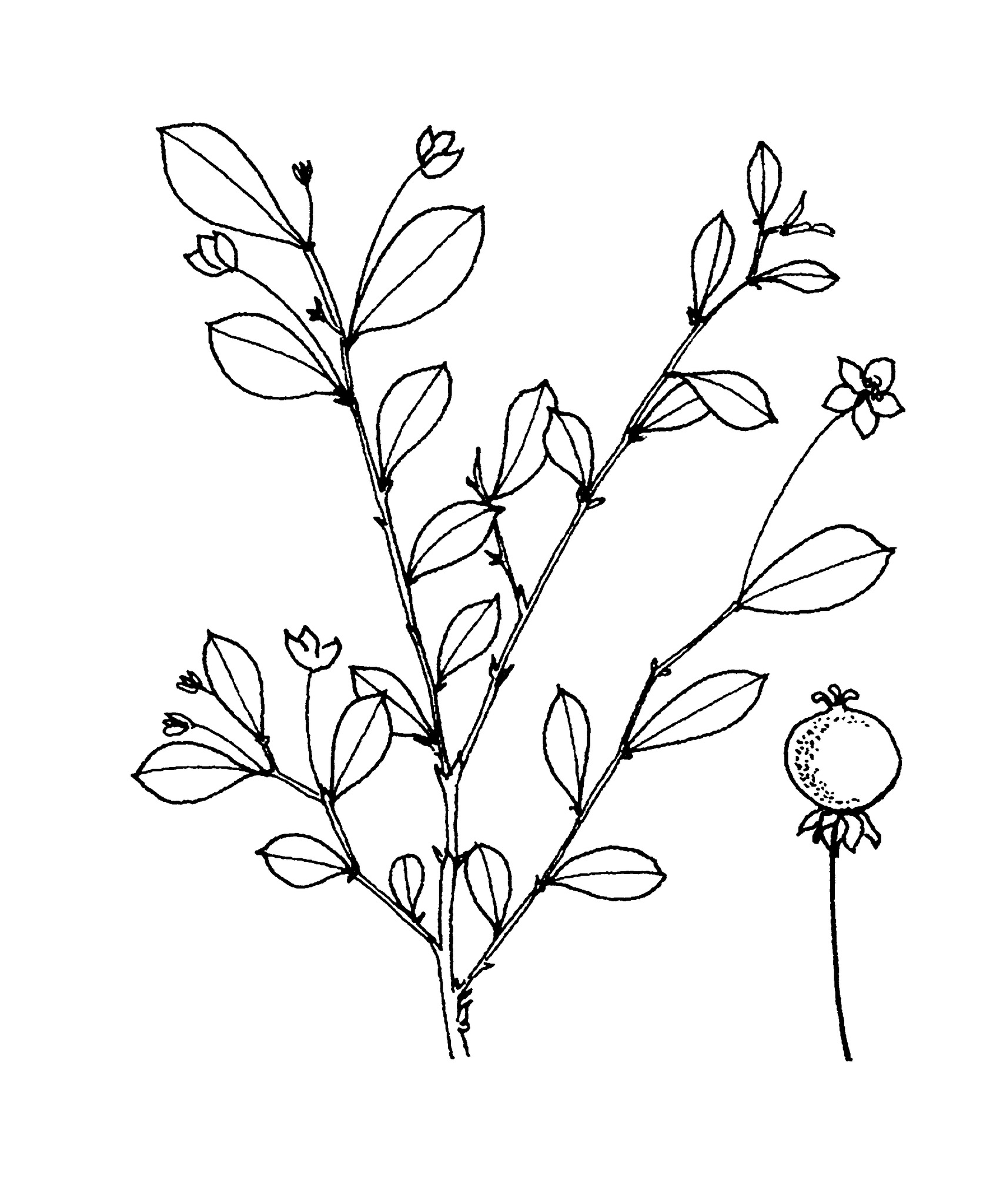
Herbs or shrubs, evergreen, perennial, male and female flowers on the same or different plants; stems and foliage without latex. Indumentum of simple, multicellular hairs. Stipules entire, inconspicuous, persistent. Leaves alternate (usually spirally arranged on branches), stalked, unlobed, penninerved, without glands; margins entire. Inflorescences axillary, with solitary or clustered flowers.male flowers stalked; calyx lobes 3, edge to edge, free or partially fused; petals 3, free or partially fused; disk absent; stamens 3, filaments fused. Female flowers stalked; calyx lobes 3, edge to edge, free or variously fused; petals 3; disk absent; ovary 3-chambered, ovules 2 per chamber; styles 3, free, entire or divided into 2. Fruits capsular, dehiscent, 3-lobed, surface smooth. Seeds 3-angled, ecarunculate.
About 50 species worldwide with 25 species in Australia. 2 Australian species are commonly cultivated.
Seed.
Leaves spirally arranged on branches; flowers without disk; stamens 3, filaments fused; styles 3, free.Very similar to Phyllanthus, mainly differing in having no disk in the flowers.
Source: (2002). Euphorbiaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 3. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 2. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
