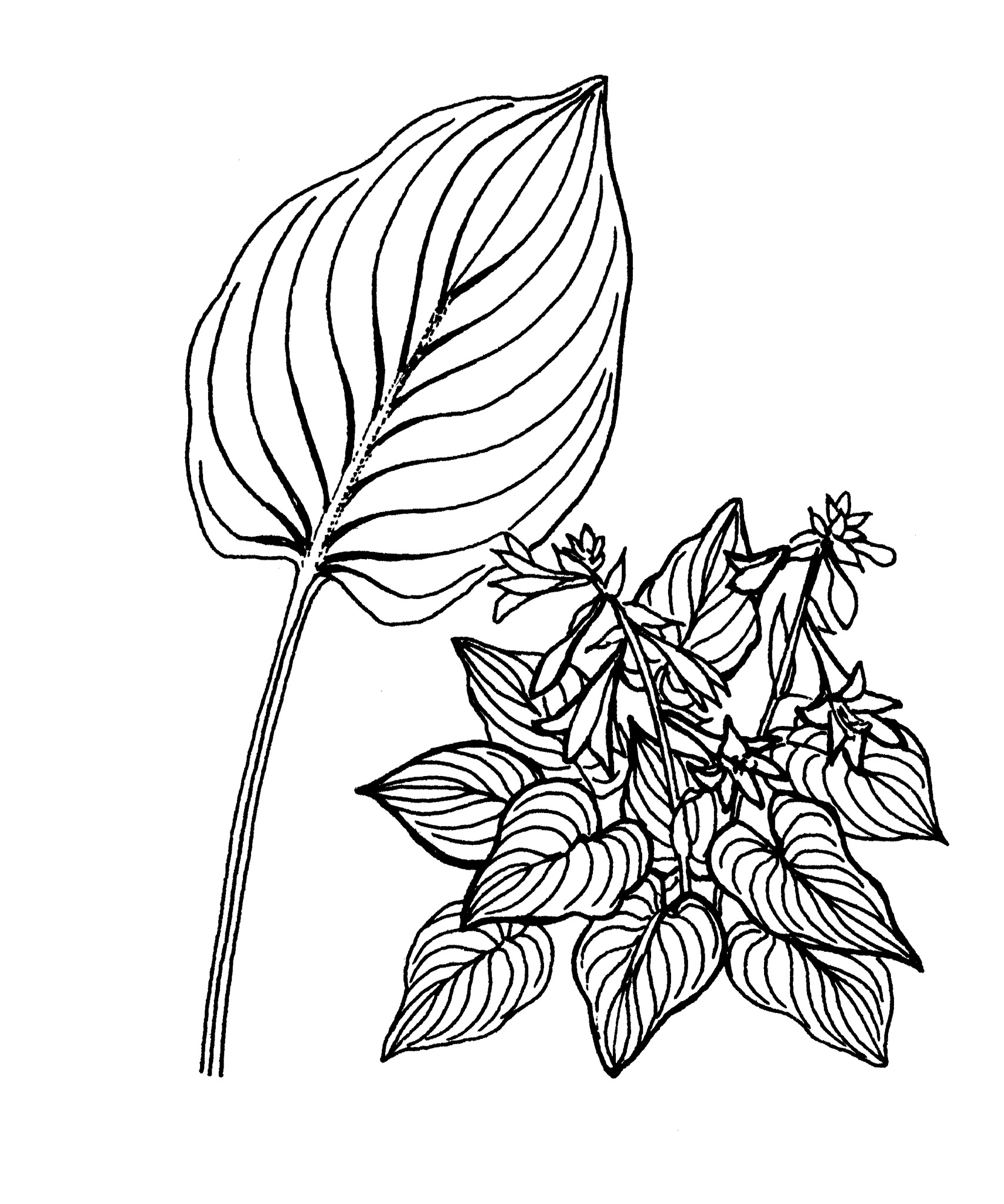
Perennial thick-rooted rhizomatous herbs. Leaves simple, entire, broadly ovate, basal. Flowers radially symmetrical, bisexual, numerous, in terminal stalked racemes.Tepals 3+3, united basally; individual flower stalks articulated. Stamens 6, free or attached to the base of the tepals. Ovary superior, 3 chambered with numerous ovules. Fruit a many-seeded, dry dehiscent capsule. Seeds ovoid, black, without arils.
A large number of currently popular species and cultivars. Growth is best in moist shade.The leaves are appealing in borders for their formal rosettes, variegations and parallel veins.
Between 25 and over 40 species (depending on species concept) from China, Japan, Korea and Russia.
Broad, stalked rosettes of decorative parallel-veined leaves and racemes of flowers with basally united, unspotted tepals.
Hensen (1985), Schmid (1991, 1999), Aden (1992), Grenfell (1993), Bond (1994). Cultivars: American Hosta Soc. (1993).
Source: (2005). Hostaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 5. Flowering plants. Monocotyledons. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
