From the Greek keros — wax, and pege — well, alluding to the resemblance of the flowers to wax candles.
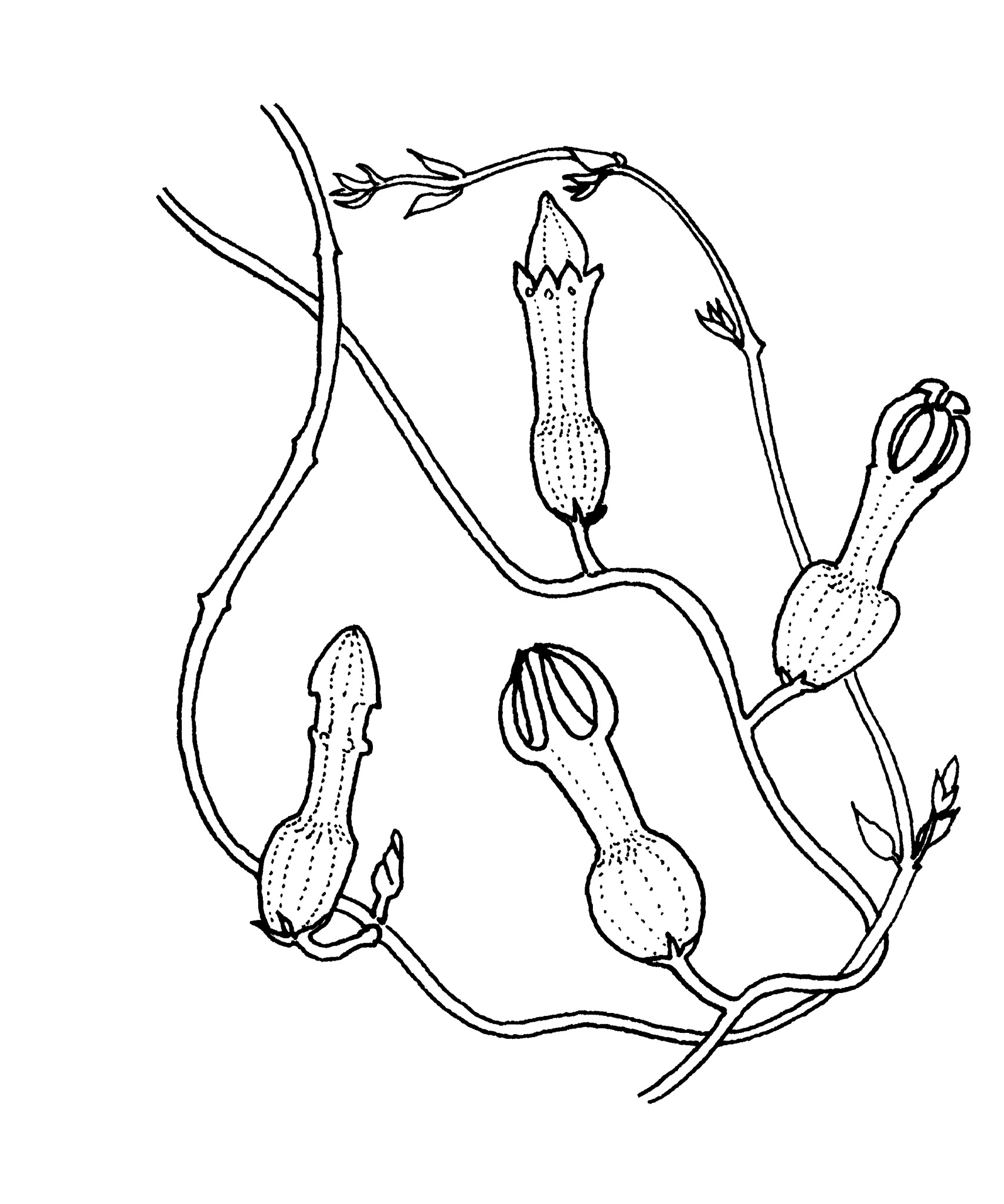
Perennial succulent herbs or twiners (often geophytic), with clear latex. Rootstocks of solid tubers, fleshy, tapered at each end, or fibrous. Leaves herbaceous to succulent; mucilage glands present. Corolla funnelshaped; tube longer than lobes, inflated at base; lobes connate or free at tips, valvate. Annular and corolline coronas absent; interstaminal corona cup-shaped, of 5 variously divided lobes that may be partially fused to the staminal corona; staminal corona of 5 lobes, connivent above style head. Follicles tapered at each end; seeds with hair tufts at one end.
The genus is best known for C. woodii, String of Hearts.
All species have peculiar lantern-like flowers that will often trap the small flies that visit them for nectar.
Seed or cuttings.
Lantern-like flowers with the corolla lobes generally fused at the tip.
Over 100 species, mainly in Africa and on the Indian subcontinent with a few outliers in Asia and Malesia and 1 native species in N Australia.
Dyer (1983), Bruyns (1985).
Source: (2002). Asclepiadaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 4. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 3. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
