From the Latin dissilio — to fly apart, referring to the dehiscence of the fruit capsule.
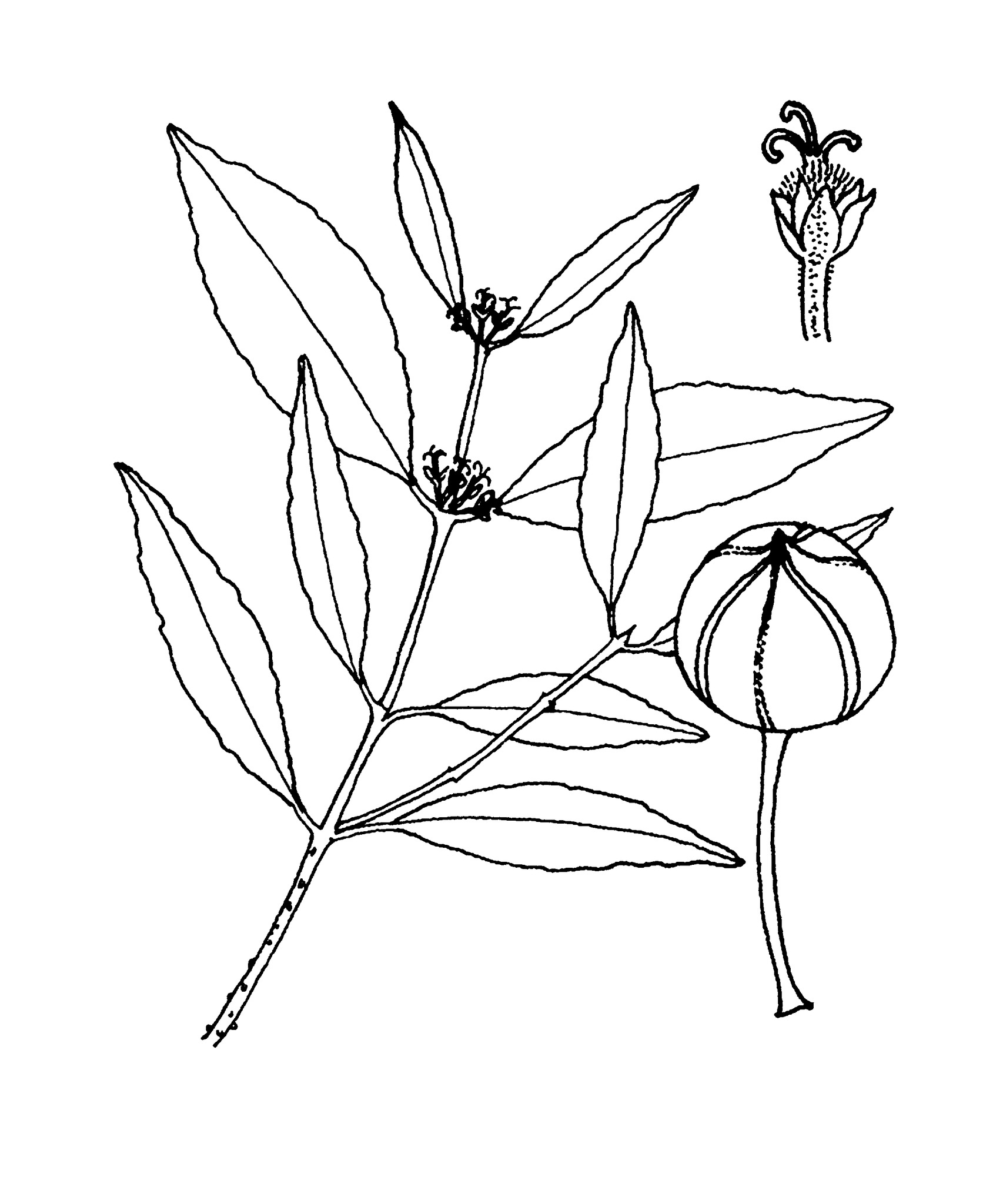
Trees, evergreen, perennial, male and female flowers on separate plants; stems and foliage without latex. Indumentum of simple, multicellular hairs. Stipules entire, inconspicuous or conspicuous, soon shed. Leaves opposite, stalked, unlobed, penninerved, without glands; margins entire or scalloped. Inflorescences axillary, racemose, solitary or fascicled, unisexual, with flowers in bracted clusters. Male flowers stalked; sepals overlapping, 3+3; petals absent; receptacle convex; disk absent; stamens 8-26, filaments free, attached to slightly convex receptacle. Female flowers stalked; sepals overlapping, in 2 groups of 3; petals absent; disk shortly annular or cup-shaped; ovary 2-3-chambered, ovules biloculate; styles 3, erect, linear-subulate, entire, shortly fused at base. Fruit capsular, dehiscent, 3-lobed, surface smooth to muriculate. Seeds semi-elliptic in outline, laterally compressed; carunculate, non-arilloid.
Endemic to Australia with 6 species. 1 species commonly cultivated.
Seeds. Intolerant of frost.
Large tree; leaves opposite; fruit muriculate; seeds laterally compressed.
Forster (1997b).
Source: (2002). Euphorbiaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 3. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 2. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
