From the latinised version of the Indonesian vernacular name, kodiho.
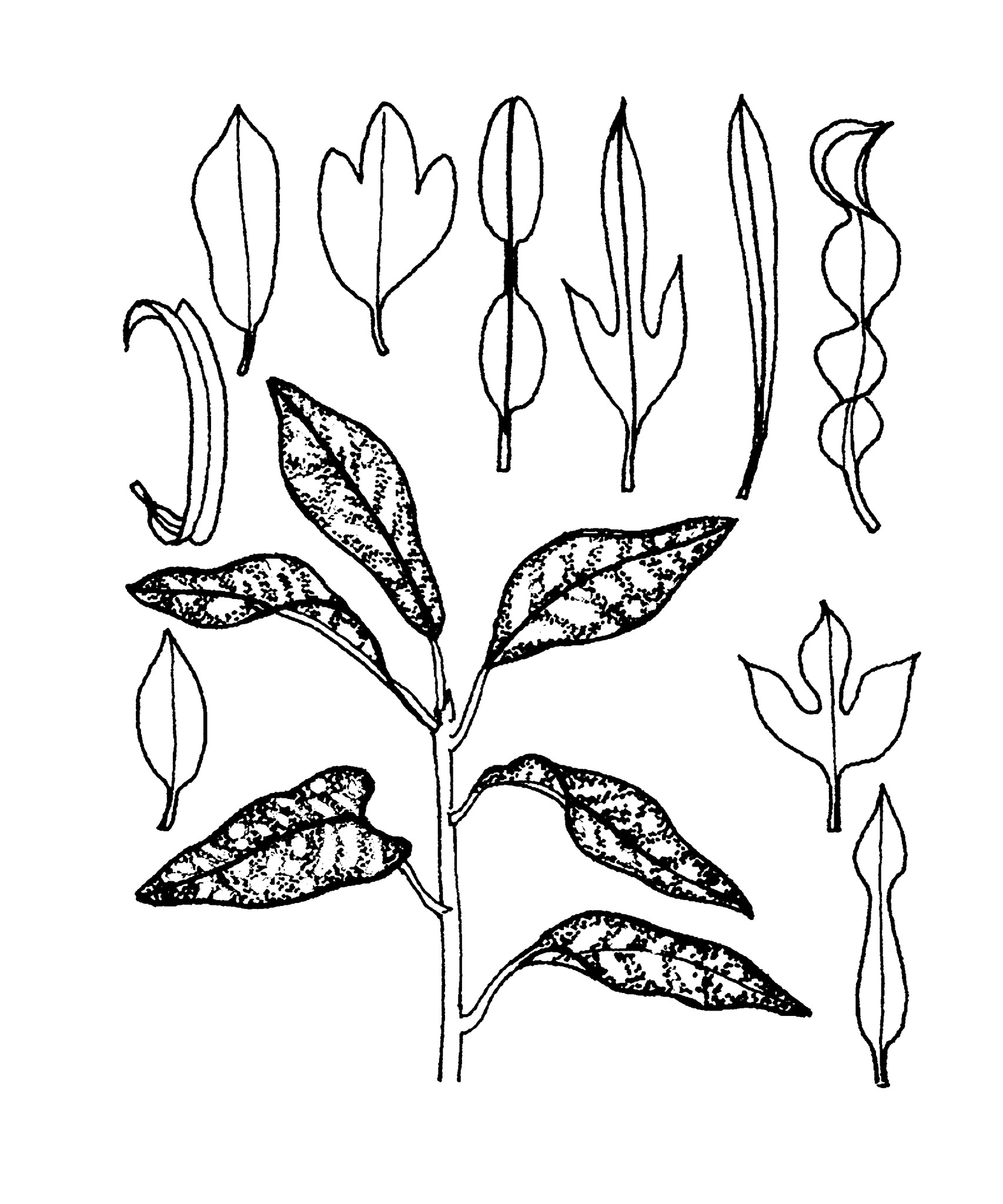
Shrubs or trees, evergreen, perennial,male and female flowers on the same plant; stems and foliage with clear to brownish latex. Indumentum of simple, multicellular hairs. Stipules entire, inconspicuous, soon shed. Leaves alternate, stalked to stalkless, unlobed, penninerved, without glands; margins entire, often wavy. Inflorescences terminal or axillary, racemose or solitary, usually unisexual, with flowers in bracted clusters with a single involucre.male flowers stalked; calyx lobes 3-6, overlapping, free and more or less equal; petals 2-6, overlapping, free; disk comprising small glands; stamens 15-100, filaments free and attached to a slightly raised receptacle. Female flowers stalked; calyx lobes 3-6, overlapping, free and more or less equal; petals absent; disk cup-shaped; ovary 3-chambered, ovules 1 per chamber; styles 3, shortly fused at base, entire or rarely divided into 2 or multifid. Fruits capsular, dehiscent, 3-lobed, surface smooth. Seeds ovoid; carunculate, non-arilloid.
About 15 species in Malesia, Melanesia and Australia (2 species). 1 exotic species is commonly cultivated.
Cuttings or seeds.
Shrubs with leaf blade wedge-shaped to obovate, elliptic, obcordate or rarely linearlanceolate, variously variegated.
Airy Shaw (1980), Ellison (1995), B.F. Brown (1996).
Source: (2002). Euphorbiaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 3. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 2. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.
