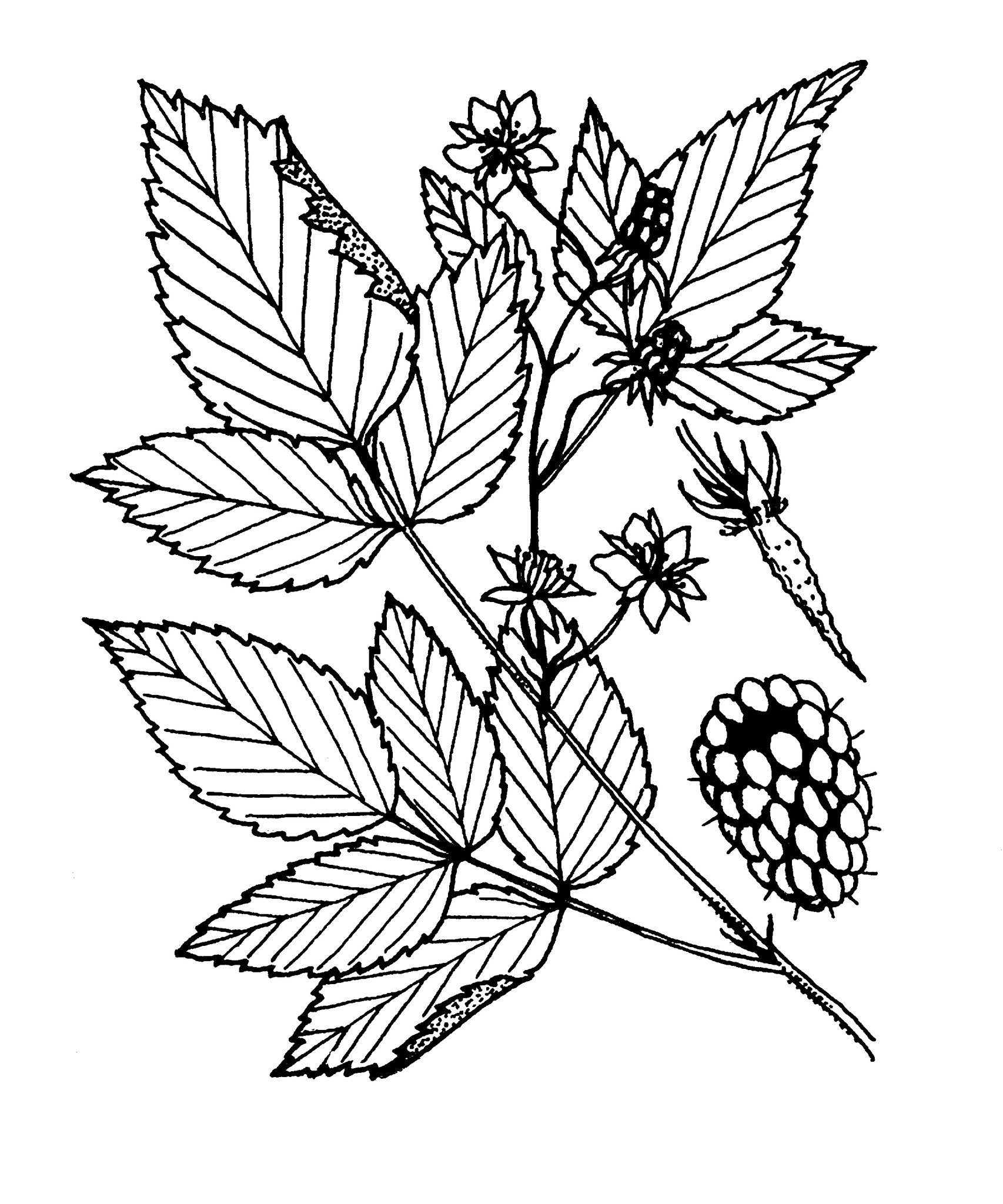
Variable shrub to about 1.5 m tall; stems with prickles, bristles and hair and waxy-blue at first. Leaves pinnate, with 3-7 ovate to oblong leaflets that are sometimes shortly lobed, cordate at the base, white-hairy below. Flowers white, in few-flowered clusters; late spring to early summer. Fruit orange to red (rarely yellowish).
Raspberries have been cultivated for the table since prehistoric times. In Australia commercial production of raspberries is on a small scale, chiefly in cooler areas of Vic and Tas. Cultivars are selected for upright thornless canes, fruit quality, shelf life (which is extremely short: generally only 3-4 days from picking to consumption), season extension and tolerance to a range of soils and climates.
The Victorian Department of Agriculture has a Raspberry breeding program and new cultivars are undergoing commercial evaluation.
N Asia, Europe.
Differing from brambles (blackberries and hybrids like the loganberries, boysenberries, youngberries and Silvan Blackberry) in having fruit that separates from the receptacle (plug).
McGregor (1998).
Other listed cultivars include 'Chilcotin', 'Chilliwak' and 'Glen Clova', with strong thornless canes; and 'Haida', 'Nootka', 'Serpell's Willamette' and 'Skeena'. 'Dinkum' and 'Bogong', released by Agriculture Victoria, fruit in the autumn.
Source: (2002). Rosaceae. In: . Horticultural Flora of South-eastern Australia. Volume 3. Flowering plants. Dicotyledons. Part 2. The identification of garden and cultivated plants. University of New South Wales Press.

This is a New York cultivar int. to Australia in 1977 as a warmer-climate selection for areas such as the n coast of nsw.
Int. from Oregon, usa, in 1972 and a major commercial cultivar, producing 2 crops per year.